Geographically and geopolitically, The Caucasus is a complex region located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia in a mountainous terrain, each country a region culturally diverse.
The Greater Caucasus lies to the north (Russian Caucasus) and the Lesser Caucasus to the south with Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan, both stretching from the Black Sea in the West to the Caspian Sea to the East.
Western Australia (WA) is the largest state in Australia, covering about 2.6 million square kilometers—nearly one-third of the continent. From arid deserts in the east to rugged coastlines and lush forests in the southwest, its landscape are diverse.
WA's climate varies significantly across its vast area. The Kimberley experience a tropical monsoon climate with distinct wet and dry seasons, while the Pilbara is characterized by a hot desert climate. The southwest enjoys a Mediterranean climate, with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. The interior is largely arid or semi-arid, with the Great Sandy, Great Victoria and Gibson Deserts.
Geologically, WA boasts some of the oldest rocks on Earth, with formations over 3 billion years old in areas like the Pilbara. Its mineral-rich geology underpins a robust mining industry, extracting iron ore, gold, nickel, and natural gas. The state is also home to significant features like the Bungle Bungle Range, karst cave systems, and extensive coastal reefs, including Ningaloo Reef, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Globe Locator Map of Namibia
Sinaloa is a Mexican state, located in northwestern Mexico, boasting a coastline stretching over 600 kilometers along the Gulf of California (Sea of Cortez). The state features a varied landscape, with coastal plains, fertile valleys, and the Sierra Madre Occidental mountain range running through its eastern side. These mountains gradually descend into expansive agricultural lands that are among Mexico's most productive.
The climate of Sinaloa varies by region. Coastal areas experience a tropical, semi-humid climate with hot summers and mild winters. The inland and mountainous regions, however, have a more temperate climate. Rainfall is concentrated in the summer months, particularly during the monsoon season.
With a population of around 3 million, Sinaloa is known for its vibrant culture, including traditional *banda* music, a regional Mexican genre that originated there. The state's culinary traditions are also notable, with seafood playing a central role, thanks to its coastal location.
Tourism in Sinaloa is focused on its beach resorts, like Mazatlán, known for its picturesque coastline, historic old town, and cultural festivals. The state is also rich in ecotourism opportunities, with mountains and forests offering outdoor activities like hiking and bird watching.
The Largest state in Mexico, Chihuahua is located in the country's north, bordering the U.S. states of Texas and New Mexico. The eastern part of the state is dominated by the Chihuahuan Desert, characterized by arid landscapes, while the western region is part of the Sierra Madre Occidental, home to deep canyons, including the famous Copper Canyon (Barranca del Cobre), a natural wonder larger and deeper than the Grand Canyon.
The climate varies significantly depending on elevation. In the desert areas, summers are extremely hot and dry, with temperatures often exceeding 40°C (104°F), while winters can be cold, especially at night. In contrast, the mountainous regions experience cooler temperatures and receive more rainfall.
Chihuahua's nature includes diverse ecosystems, from desert flora like cacti and agaves to pine and oak forests in the highlands. The state is also rich in wildlife, including pumas, black bears, and various bird species.
The people of Chihuahua have a blend of indigenous and mestizo heritage. The Tarahumara (Rarámuri) people, known for their long-distance running abilities, inhabit the remote mountainous areas. Culturally, the state reflects strong northern Mexican traditions, with a cowboy (vaquero) lifestyle, folk music, and regional dances, alongside influences from nearby U.S. border regions.
Second largest state in Mexico, Sonora lies in the northwestern part of the country, the Sonoran Desert dominating its landscape. The Sea of Cortez coastline boasts beautiful beaches and marine biodiversity. The Sierra Madre Occidental mountain range runs through the eastern part of the state, bringing elevation with pine forests.
The climate varies from arid to semi-arid, with extremely hot summers and mild winters. Coastal areas experience high humidity, while the desert sees scorching temperatures, often exceeding 40°C (104°F) in summer. Rainfall is sparse, mostly arriving during the summer monsoon season.
Sonora's nature is rich in flora and fauna adapted to desert life, including cacti, mesquite trees, coyotes, and roadrunners. The coastal waters teem with marine life.
The people of Sonora are a blend of indigenous groups like the Yaqui and Mayo, along with mestizo descendants of Spanish settlers. The culture reflects this mix, with strong indigenous influences in crafts, festivals, and cuisine.
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, spanning around 1,200km from south to north, with a maximum depth of over 1,000m. The northern part is shallow, while the southern part is much deeper, with significant oil and gas reserves beneath its floor.
The saltwater Caspian is bordered by five countries: Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, and Azerbaijan.
Geopolitically, the Caspian Sea region is strategic due to these vast energy resources. Russia and Iran influence the region, while Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, and Turkmenistan are becoming key players in energy markets.
The climate around the Caspian varies significantly. The northern shores experience cold winters and warm summers, while the southern shores, closer to Iran, have a more arid climate.
Culturally, the region is a mix of Turkic, Persian, Slavic, and other ethnic influences. People are often tied to fishing, oil industries, and agriculture. The diverse cultural heritage reflects Islamic, Orthodox Christian, and secular influences.
The Balkans is a mosaic of ethnic groups, languages, and religions, with Slavic, Albanian, Greek, and Turkish influences, Eastern Orthodoxy, Islam, and Roman Catholicism being the major religions. This diversity has fostered rich traditions in music, dance, and cuisine but has also been a source of historical tension.
Geopolitically, the Balkans has been a flashpoint for conflicts, particularly during the 20th century. The dissolution of Yugoslavia in the 1990s led to the creation of new states. Today, the region remains politically complex, showing varying degrees of economic development, EU integration, and unresolved ethnic tensions, particularly in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kosovo.
The US-Mexico border stretches 1,954 miles from the Pacific Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico, spanning diverse geographical landscapes. The westernmost portion begins at the Pacific, crossing through the urban areas of San Diego, California, and Tijuana, Baja California. As it moves eastward, the border traverses mountainous terrain, notably the rugged peaks of the Sierra Madre and the Sonoran Desert, with harsh, arid conditions and sparse vegetation.
Further east, the border follows the Rio Grande River, which serves as a natural boundary between Texas and the Mexican states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas. This section features varied landscapes, including desert basins, rolling plains, and river valleys. The Rio Grande’s meandering path creates a mix of floodplains and steep canyon walls, making parts of the border difficult to navigate.
Urban crossings, such as those in El Paso, Texas, and Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, are among the most heavily trafficked, blending bustling cityscapes with high-security infrastructure. The border concludes at the Gulf of Mexico, where marshlands and coastal plains dominate, marking a stark contrast to the arid deserts of the western border.
The islands of the Indian Ocean range from coral atolls in the Maldives to volcanic islands like Reunion and Mauritius. Madagascar, the largest island, features diverse ecosystems including rainforests, deserts, and unique flora and fauna. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands, part of India, harbour dense forests and indigenous tribes. These islands are strategically significant due to their locations along key maritime routes.
The main islands are:
Madagascar, Mauritius, La Reunion (FR), Comoros Islands, Mayotte (FR), Kerguelen (FR),
Chagos Archipelago (UK), Seychelles, Rodrigues, Andaman (India), Nicobar (India),
Maldives, Cocos Islands (Australia)
The Caribbean Islands is made of over 7,000 islands, islets, reefs, and cays.
The major islands and archipelagos include the Greater Antilles, comprising Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola (Haiti and the Dominican Republic), and Puerto Rico, and the Lesser Antilles, which include the Leeward Islands, Windward Islands, and the ABC Islands (Aruba, Bonaire, and Curaçao).
Geographically, the islands vary from flat coral islands to mountainous volcanic islands. The region is known for its tropical climate, beautiful beaches, and diverse ecosystems, including rainforests, mangroves, and coral reefs.
Geopolitically, the Caribbean is a diverse mosaic of independent countries, overseas territories, and dependencies. Key independent nations include Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago, and Barbados, while significant territories include Puerto Rico (U.S.), Guadeloupe and Martinique (France), and the British Virgin Islands (U.K.). The region's strategic location has historically made it a focal point for colonial powers, and it continues to be of geopolitical interest due to its proximity to major shipping routes, its economic reliance on tourism, and its diverse cultural heritage.
Three countries in Africa are named Guinea: Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, and Equatorial Guinea.
This can be traced back to historical and colonial influences. The term "Guinea" itself originates from the Berber word "Akal n-Iguinawen," which means "Land of the Black Men," and was used by Europeans to describe the West African coast.
Guinea: Formerly French Guinea, gained independence from France in 1958. It is the largest of the three and lies directly on the west coast of Africa. Its capital is Conakry and Guinea is also referred as Guinea Conakry.
Guinea-Bissau, originally a Portuguese colony, added its capital, Bissau, to its name upon independence in 1973 to distinguish itself from neighboring Guinea. It is situated north of Guinea on the Atlantic coast.
Equatorial Guinea, which is located on the central African west coast and comprising a mainland region and islands, was formerly known as Spanish Guinea before gaining independence from Spain in 1968. Its name reflects its location near the equator.
The overlapping colonial histories and the broad European use of "Guinea" to describe this region led to multiple countries adopting similar names, each modified to reflect their unique colonial legacies and geographic distinctions.
Africa's vegetation is highly diverse, reflecting its varied climate and geography. In the northern part of the continent, the Sahara Desert dominates, characterised by sparse vegetation such as drought-resistant shrubs and grasses. Moving south, the Sahel region marks a transition zone with semi-arid conditions, supporting grasses, acacias, and scattered shrubs. Further south, the tropical rainforests of Central Africa, particularly in the Congo Basin, represent one of the world's largest continuous forest zones. These rainforests are dense with tall trees, lianas, and a rich understory of shrubs and herbs. Surrounding the rainforests are moist savannas with a mix of grasses and trees, including baobabs and acacias. East Africa's highlands and rift valleys feature diverse vegetation from montane forests to savannas, influenced by altitude and rainfall variations. The coastal areas, particularly along the eastern coast, have mangrove forests, while the southern tip of Africa, including parts of South Africa, boasts the unique fynbos biome, rich in endemic plant species. Southern Africa also hosts vast savannas and grasslands, with the Kalahari Desert introducing semi-arid vegetation. Each of these regions supports distinct ecosystems and biodiversity, making Africa's vegetation a complex mosaic influenced by its climatic and geographical diversity.
The Russian Far East region of Kamchatka is a land of fire and ice, graced by dramatic landscapes dominated by a chain of active volcanoes. The remote peninsula boasts over 300 volcanoes, 29 of which are still active with Klyuchevskaya Sopka being the highest volcano in Eurasia. The region's geography is characterized by rugged terrain, vast tundra, and abundant wildlife, with brown bears and salmon-filled rivers. The road network is extremely limited. Kamchatka is on the same time zone with New Zealand, two hours ahead of Australia.
The weather in Kamchatka is harsh, with long, cold winters and short, cool summers. Despite the challenging climate, the indigenous people of Kamchatka, primarily the Koryaks, Itelmens, and Evens, have adapted to the environment over centuries, relying on fishing, hunting, and reindeer herding for sustenance. Traditional culture thrives in Kamchatka, evident in rituals, folklore, with intricate beadwork and woodcarving.
The people of Kamchatka, while embracing modernity, maintain a deep connection to their ancestral roots, preserving their languages and customs. Russian settlers have also influenced the region's culture, contributing to a unique blend of indigenous and Russian traditions.
The Colorado River is one of the most iconic waterways in North America, meanders through the southwestern United States, carving its way through arid landscapes and shaping some of the continent's most spectacular geological features. Originating in the Rocky Mountains of Colorado, it begins as a modest stream fed by melting snow and glacier runoff.
As it courses through seven U.S. states—Colorado, Wyoming, Utah, New Mexico, Nevada, Arizona, and California—the river gains momentum and volume, eventually reaching its terminus in the Gulf of California (Sea of Cortez) in Mexico. Along its journey, the Colorado River serves as a lifeline for millions of people, providing water for agriculture, industry, and urban centers in an otherwise parched region.
The river's importance extends beyond its role as a vital water source; it also boasts a rich ecological heritage. Its waters support a diverse array of plant and animal species.
The Colorado River has shaped the dramatic landscapes of the American Southwest, carving iconic features such as the Grand Canyon, Glen Canyon, and Hoover Dam, leaving a lasting imprint on the region's geography and culture.
The Red Sea is a long, narrow, and relatively shallow body of water located between northeastern Africa and the Arabian Peninsula.
It connects to the Mediterranean Sea via the Suez Canal in the north and to the Indian Ocean via the Bab-el-Mandeb strait in the south.
It stretches approximately 2,250 km in length from its northern tip to its southern end. Its width varies, but it averages around 355 km at its widest point.
The Red Sea is believed to have formed as a result of tectonic activity associated with the separation of the African and Arabian plates. This process began around 30 million years ago and is still ongoing, causing the Red Sea to widen by a few centimeters each year.
There are several islands within the Red Sea, although they tend to be relatively small. Some notable ones include the Dahlak Archipelago off the coast of Eritrea, the Farasan Islands off the coast of Saudi Arabia, and the Zubair Group near Yemen.
The Red Sea region experiences a hot desert climate with high temperatures year-round. Rainfall is generally scarce, particularly in the northern and central parts of the sea. It is home to a diverse array of marine life, including colorful coral reefs, fish species, marine mammals, and invertebrates. Its unique ecosystem is characterized by high levels of endemism, with many species found nowhere else in the world.
The Red Sea has been an important trade route for centuries, linking the Mediterranean world with the Indian Ocean and beyond. Major ports along its shores include Jeddah in Saudi Arabia, Port Sudan in Sudan, and Djibouti City in Djibouti. Additionally, tourism, fishing, and offshore oil and gas extraction are significant economic activities in the region.
In the French language, nouns have a gender, either feminine or masculine. This applies also to country, state or region’s names.
In the case of the US States, 9 states are “feminine”, the rest is masculine. There is no gramatical rule.
By default, the noun “state” is masculine (un état), thus all states are masculine, except those bearing a feminine name and/or ending in ‘ie” in French ie Virginie x2, Caroline x2, Californie, Georgie, Pennsylvanie. Florida and Louisiana are also feminine, which could have an historical origin set before entry into the Union, as La Louisiane was French and La Florida Spanish.
Baja California Sur is located in northwestern Mexico, on the southern half of the Baja California Peninsula, surrounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Gulf of California to the east. It is one of the 26 states of Mexico.
The geography of Baja California Sur is marked by rugged mountains, expansive deserts, and a striking coastline. The Sierra de la Giganta mountain range runs through the center of the region, providing a dramatic backdrop to the arid desert landscapes. The coastline boasts pristine beaches, rocky cliffs, and vibrant coral reefs, making it a haven for marine life.
The climate of Baja California Sur is predominantly arid and semi-arid. Summers are hot and dry, while winters are mild, creating an appealing year-round destination for visitors. The Gulf of California (Sea of Cortez) moderates temperatures along the eastern coast, fostering a more temperate climate in cities like La Paz.
The wildlife in Baja California Sur is diverse and adapted to the harsh desert environment. The Gulf of California is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a critical habitat for marine life, including dolphins, whales, and a variety of fish species.
Baja California is located in the northwestern part of Mexico, boasts a diverse range of geographic features that contribute to its unique character. The region spans from the Pacific Ocean on its western border to the Gulf of California (Sea of Cortez) on the east, with the Baja California Peninsula extending southward for approximately 1,600km. Its landscape includes stunning desert terrain, mountain ranges like the Sierra de San Pedro Mártir, Sierra de la Giganta and beautiful coastal areas.
Administratively, the peninsula hosts two states, Baja California in the North and Baja California Sur in the South.
The climate varies from Mediterranean along the coast to desert further inland. The coastal areas enjoy mild, pleasant temperatures, making them popular tourist destinations year-round. However, the interior regions experience hot, arid conditions with minimal rainfall. The peninsula is home to many endemic plants, million of cacti of all shape and form grace its unique and stunning landscape.
Baja California is home to a population that is a mix of indigenous groups, Mexicans from other states, and a growing expatriate community. Tijuana and Mexicali are the largest cities, serving as economic and cultural hubs. La Paz is the largest city in the South. The state embraces a blend of Mexican and American influences, especially in border towns, creating a vibrant cultural fusion.
Tourism is a significant industry in Baja California, attracting visitors with its beautiful beaches, diverse marine life (Gray, blue and shark whales), diving, surfing, kite surfing, fishing activities, and thriving culinary scene. Ensenada is known for its wineries, while Cabo San Lucas offers luxury resorts and sport fishing opportunities. The state also hosts events like the Baja 1000 off-road race, drawing adrenaline seekers from around the
The countries of West Africa - Can you name and place them on the map, name their capital cities?
Map of Morocco illustrating an architecture book showcasing Morocco’s architectural masterpiece, scattered around the country.
The Arabian Peninsula has a diverse geography, rich cultural heritage, unique climate, and distinct landscape. Stretching over 3.2 million sq km, it encompasses several countries, including Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Bahrain, and Qatar. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula is marked by vast deserts, such as the Rub' al Khali (Empty Quarter) and An-Nafud, which dominate its interior. Towering mountain ranges like the Hijaz Mountains along the Red Sea coastline and the Asir Mountains in the southwest provide relief from the arid expanses. The peninsula is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and the Arabian Sea to the south, influencing its climate. The climate varies from arid to semi-arid, with scorching temperatures during summer and cooler winters. Sandstorms are common in the desert regions. The people of the Arabian Peninsula have adapted to this challenging environment, engaging in traditional activities like camel herding and oasis agriculture. Culturally, the Arabian Peninsula is a melting pot of diverse ethnicities and languages. It holds immense significance as the birthplace of Islam, home to the holy cities of Mecca and Medina. The region's history is intertwined with ancient trade routes, fostering a rich heritage of commerce, hospitality, and oral traditions. The landscape is characterized by vast sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and wadis (dry riverbeds). Oasis settlements, often surrounded by palm groves, offer respite and sustenance. Modern cities like Riyadh, Dubai, and Doha juxtapose traditional architecture with towering skyscrapers, showcasing the rapid development of the region. The Arabian Peninsula presents an awe-inspiring blend of geographical wonders, cultural legacies, climatic extremes, and evolving landscapes that together create a captivating and enduring identity.
Africa is a vast and diverse continent with stunning landscapes, rich history, vibrant cultures and abundant wildlife. Spanning over 30 million sq km, it is the second-largest continent, housing 54 recognised countries and a plethora of unique regions.
Tourism in Africa is a captivating experience. From the majestic Sahara Desert in the north, to the lush rainforests of Central Africa and the iconic savannas of East Africa, the continent offers a wide array of natural wonders. Wildlife enthusiasts can embark on thrilling safaris to witness the "Big Five" – lion, elephant, buffalo, leopard, and rhinoceros – in their natural habitats, while adventurers can explore ancient ruins like the Pyramids of Egypt or dive into the azure waters of the Indian Ocean.
Africa's population is incredibly diverse, comprising over 1.3 billion people of various ethnicities, languages, and traditions. Major cities like Cairo, Lagos, Johannesburg, and Nairobi showcase modern infrastructure and a blend of traditional and cosmopolitan lifestyles.
Culture in Africa is as diverse as its landscapes. Each region boasts its own unique traditions, music, dance, and art forms. Traditional ceremonies and festivals, such as the Masai Mara in Kenya or the Ouidah Voodoo Festival in Benin, offer a glimpse into the continent's cultural tapestry.
Despite its incredible potential, Africa faces challenges. Nonetheless, the continent's resilience, warm hospitality, and the wealth of its heritage continue to captivate and inspire travellers from around the world, making Africa a destination like no other.
The “Stans” refers to the nations whose names conclude with the Persian suffix "-stan," which means "land of" or "place of."
#Afghanistan : Diverse ethnic groups and complex history #Kabul
#Kazakhstan : World's largest landlocked country, rich in natural resources#nursultan
#Kyrgyzstan : Stunning mountain landscapes and nomadic traditions #Bishkek
#Pakistan : 6th most populous country in the world, from coast desert the highest peaks in the world #Islamabad
#Tajikistan : Mountainous terrain, turquoise lakes, home to the Pamir Mountains. #dushanbe
#Turkmenistan : Vast deserts and natural gas reserves #ashgabat
#Uzbekistan : Rich history, architectural wonders, including the ancient city of Samarkand. #tashkent
La Ruta 40
Established in 1935, mythical Ruta 40 crosses Argentina from South to North, running along the slopes of the Andes. Its alignment, over 3,100 mi (5,000 km) long goes through three of Argentina's regions. Its magnificent sceneries, its length, the height it reaches (16,050 feet - 4.895 meters- above sea level) and the variety of regions that it crosses make it a destination in itself.: Cuyo, Patagonia and the Northern Region, and eleven provinces.
Ruta Nacional 40 (Ruta 40): From La Quiaca (Jujuy) to Cabo Virgenes (Santa Cruz)
Length: 5,224km
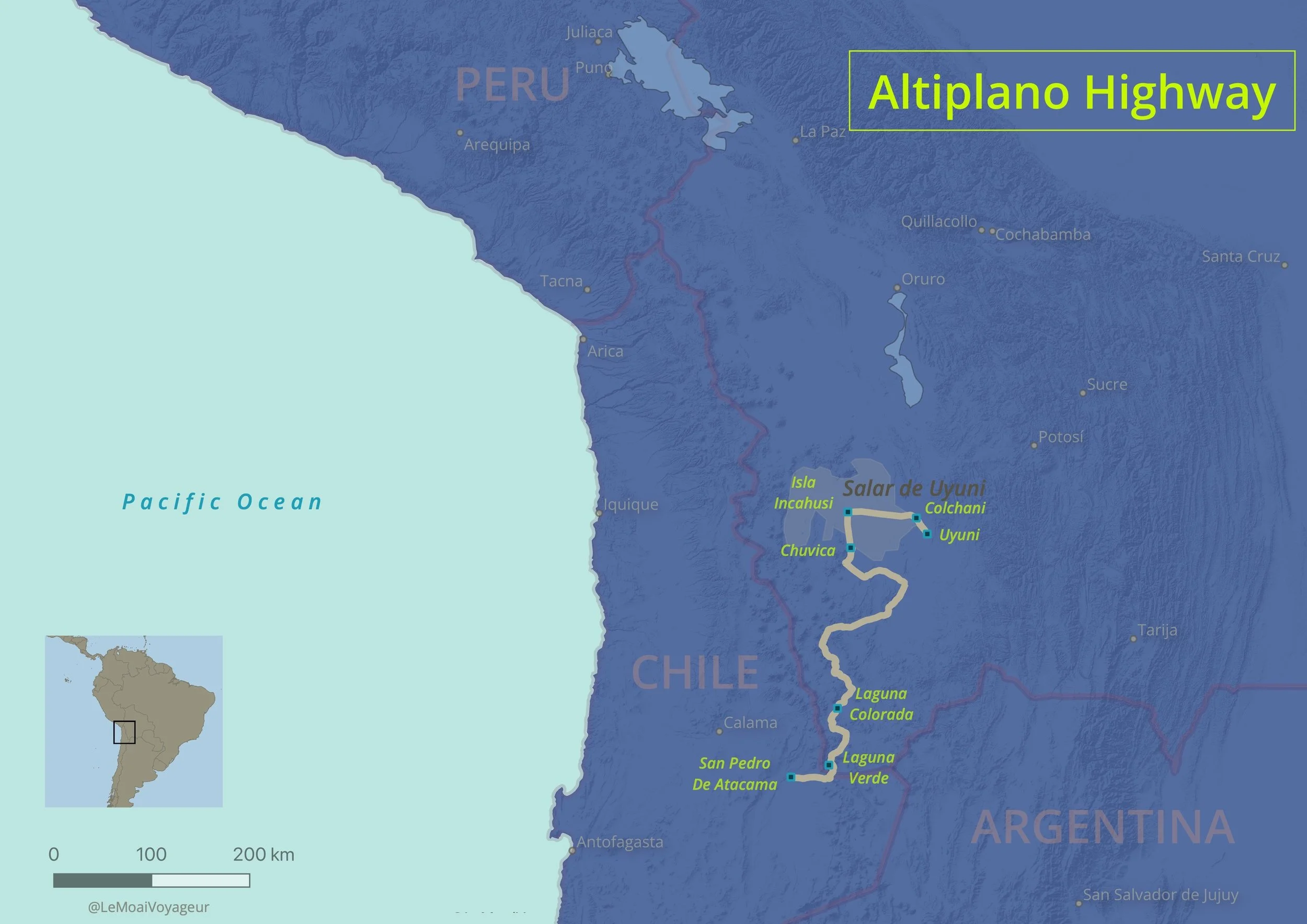
Altiplano Highway - San Pedro de Atacama (Chile) to Uyuni (Bolivia)
f you are up for the road trip of a lifetime then the border area of Chile and Bolivia has a surprise for you. The road between San Pedro de Atacama, in Northern Chile and Uyuni, Southern Bolivia is like no other road in the world, crossing high altitude dry bare landscapes, perfect cone shaped volcanoes, multicolour lagoons, hot springs and geysers. The first section of the road is paved for several kilometres, up to the border, then the road becomes a track where the real adventure begins. The magnificent Licancabur Volcano towering 5000m over San Pedro De Atacama, beckons over the entry of the “Altiplano Highway” like a sentinel watching over the jewels of the Eduardo Avaroa Reserve, Laguna Verde (Green Lagoon), which deep green colour will leave you speechless. Driving on slowly the track takes you through the most amazing landscape which seems to have been painted by an artist, where the red orange mineral colour of the surrounding mountains meet the clearest and immense blue sky. First you reach a hot spring area followed by the Geysers of Sol de Mañana where you can observe an intense volcanic activity.
If you prefer red over green, just wait. The track takes you to Laguna Colorada (Red Lagoon) where pink flamingos await for you. Relax and spot three different species of flamingos. The red colour of the lagoon is produced by an active algae which reacts to the sun light and the wind. The pink colour of the feet and feathers of the flamingos is also produced by the same algae, which is their basic food.
The best is yet to come as you dirve north and reach the “shore” of the Salar de Uyuni, the largest salt lake in the world. You will never forget this amazing sight. An endless sea of salt surround by mountains and volcanos. The Salar experiences a dry and a wet season, and looks like a giant mirror after the rain. There are a few “islands” scattered around the Salar, the most iconic is Incahuasi, which is “populated” by thousands of giant cacti that can reach 10m high. The colours, the light, the sounds and the peacefulness of this area will stay with you forever.
US states with perfectly straight border lines
Colorado, Utah and Wyoming not only share a common tri state border, they also are the only states in the federation to have perfectly straight border line. Well, nearly, given the curve of the earth!
US state border quadripoint
Utah, Colorado, Arizona and New Mexico all join together in one spot called “four corners”. It is the only point in the USA shared by 4 states, and it features a dedicated momunent where you can hop effortless from one state to the next.
English Premier League
Geographic distribution of English Premier League clubs across England,
Africa Quadripoint
The rare confluence of 4 nations in one spot exists only in Africa
#namibia #zimbabwe #zambia #botswana
Click to enlarge
NP National Park NM National Monument SP State Park TP Tribal Park NRA National Recreational Area
USA - America Southwest - Natural Wonders scenic road loop
The Southwest corner of the United States of America offers one of the largest concentration of natural wonders, most of them easily accessible by roads and fully catered to accommodate the needs of the intrepid travellers. While wild animal safary goers look for the big fives, Utah has its own: Zion, Bryce Canyon, Capitol Reef, Arches and Canyonland Nationak Parks, boosting one of the most grandiose and spectacular landscapes on earth. These giants must not overshadow lesser known yet equality splendid areas such as Natural Bridges NM, Valley of the Gods, Glen Canyon NRA, Grand Staircase-Escalante NM, Kodachrome Basin SP and Bears Ears NM. Arizona will enchant the eyes with the unmatched Grand Canyon NP, Nevada with its Valley of Fire SP. Close the loop with some of California finest treasures, Yosemite NP, Joshua Tree NP and Death Valley NP.
Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia
The 1,250km long Kamchatka Peninsula is located in Far Eastern Russia, East of the Siberia region, on the “Pacific ring of fire”, with the Sea of Okhotsk and the Pacific Ocean on each side. One of the world’s few remaining wilderness, this new frontier is a world of native people, ice and fire, and abundant wildlife. With an area of 270,000 km2 Kamchatka boast more than 30 active volcanos. Roads are few, and the most popular mode of transport is old style Russian helicopter or reindeer powered sledge. On the weather front, the peninsula is subject to about 20 distinct climatic zones, has a strong oceanic influence, with high annual precipitation, mostly in the form of snow, with cool summer and continental boreal climate.
The main city, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, is situated on Avacha Bay, unsurprisingly surrounded by a dramatic background of volcanoes.
The wildlife is plenty, consisting of bear, fox, wolf, birds, seal, sea-lion, Orca and lots of salmon.
Baja California
Baja California is a land of sheer unspoiled beauty. Lesser known than its American sister Baja, as it is affectionately nicknamed, is the original “California”. Nested alongside mainland Mexico, the Pacific Ocean on one side, the Sea of Cortez on the other, and mountains range or sierras occupying its hinterland, the peninsula is jammed packed and blessed with a rich native people culture, stunning landscapes, abundant wildlife, and eternal sunshine. Of 4,000 types of plants, 600 are endemic to the area. It is home to 120 species of cacti, 80 endemic ones, where the Cardon cacti reach up to 30m high. Many cacti flower after the rain offering an unforgettable spectacle to the traveler. The climate is mostly dry, warm and sunny, with the Pacific coastline cooler than the Sea of Cortez side’, occasional tropical storm and hurricane lash their fury in the South. The food scene is rich with Mexican traditional cuisine.
Baja California is rich of a 11,000 years strong indigenous history; following the European conquest, the Jesuits were the first missionaries, followed by the Franciscans and the Dominicans, leaving a legacy of 27 missions scattered on the peninsula. Mexico gained its independence from Spain in 1821 and Baja people proudly display their unique cultural identity. Northern Baja California (Baja California) became the 29th state of Mexico in1952 and South Baja California (Baja California Sur) became a state in 1974, both states being divided by the 28th parallel.
US Interstate Highway System (Primary Interstates)
The US Interstate Highway System criss-crosses the United States with 80,000 kilometres of rolling asphalted lanes through a well laid out grid network. Started in 1956 under the leadership of President Eisenhower, it was proclaimed completed in 1992, however the latest addition, I-11 between Boulder and Las Vegas, was completed in 2018. Funded by the Federal Government, owned by the States, the construction has been a marvel of planning and engineering, but at time faced local opposition and marred by political battles. The longest (East-West) interstate is I-90, spanning 4,861km from the Pacific Coast in Seattle to the East Coast in Boston, while the longest North-South interste is I-95 with 3,071km from the Canadian border all the way down to Miami.
To make it easy for the driving public and users, the system is cleverly organised. The network is divided into primary one and two digit interstate (this map), auxiliary three digit interstate serving urban areas. Fully integrated into the system, yes not connected to it, Hawaii, Alaska and Puerto Rico have their own numbering system.
North-South interstates are odd numbered, ascending from the West Coast to the East, East-West interstates are even numbered, ascending from the border with Mexico to the border with Canada. All exits are numbered, usually coinciding with the nearest miles market. Highway signs follow the same format, use specific fonts, and the interstate number shield has become an iconic landmark.
Basque Country
Shared by France and Spain, nested at the Southern end of the Bay of Biscay, the Basque Country boasts the unique cultural identity, language, food and tradition of the Basque people. This land of mountains, mist and green pastures, beaches, surf, bays and rocky coastline, is divided into 7 regions:
.Northern Basque Country (France) or “Pays Basque” in French or “Iparralde” in Basque, made of:
-Labourd (Ustaritz); Basse Navarre (St-Jean-Pied-De-Port; Soule (Mauléon)
Southern Basque Country (Spain) or “País Vasco” in Spanish or “Hegoalde” in Basque, made of:
*Autonomous Community of the Basque Country, divided into:
Alava (Vitoria-Gastiez); Bizkaia (Bilbao); Gipuzkoa (Donostia-San Sebastian)
*-Navarra (Pamplona)
The Basque Country enjoys a mild climate, temperated by the Gulf Stream waters, with year round rainfall giving the landscape a lush green appearance. The Basque People have a strong regional identity and a craving for independence. There are about 3 millions people living in the Basque Country and a large Basque diaspora is scattered around the world, mainly North and South America.
Villes Impériales
From Boulogne-Sur-Mer in the North, to Nice in the South, 20 French Cities (21 including Sainte-Hélène Island) share a strong heritage and connection with the First and Second Empires. These 2 quintessential eras of French history feature a strong influence from Napoleon I and his nephew Napoleon III whose leadership lead to a legacy of splendid buildings and architecture wonders.
Africa
This map is specially designed to illustrate Siân Pritchard-Jones & Bob Gibbons travel guide “ A Pictorial Guide to Africa Overland” available for purchase on Amazon.
The geopolitic of the Caucasus.
The Caucasus is a region of sheer beauty, nested between East and West, Europe and Asia, niched between the Caspian and the Black seas, rich of ancient civilization and culture, stunning landscape, delicious food and wine, and above all, inhabited by fiercely proud and independant people, speaking a myriad of different languages.
The Caucasus spans over the following political areas:
9 Russia administrative regions (North Caucasus, or Russian Caucasus):
Dagestan ; Chechnya; Ingushetia; North Ossetia; Kabardino Balkaria
Karachay Cherkessia; Krasnodarsk; Stavropol'; Adygea
3 countries:
Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan.
Within those countries, 3 regions have drawn attention, Abkhazia and South Ossetia in Georgia, for their strong independence desire, and Nagorno Karabakh in Azerbaijan which is claimed by Armenia.
The Karakoram and Pamir Highways
Kurdistan
If Kurdistan was a country, it could look like this region where more than 60% of the population is inhabited by Kurds.
It would spans parts of modern-day Iraq, Turkey, Iran, and Syria in the regions where the Kurdish people represent the largest groups.
From a geography perspective, the region is diverse, featuring rugged mountains amongst them the Zagros and Taurus ranges, rolling plateaus, fertile plains, and rivers with the the Tigris and Euphrates. With such natural variety the region supports agriculture, with wheat, barley, and fruits, while its mountains offer breathtaking landscapes, canyon, hiking trails and resources like oil and minerals.
The Appian Way
When construction began on the Appian Way in 312 B.C., it was the first of 29 highways fanning out from Rome that inspired the saying “ All roads lead to Rome”. It would later stretch hundreds of miles to the port city of Brindisi. The 2,300-year-old Via Appia was built to transport armies of ambitious Roman statesmen. After serving as a pathway for troops, merchants, and pilgrims for centuries, the Appia fell into disuse. Today much of it is buried under farms, highways, and modern construction.
While it has been obscured by modern Italy, an ambitious government plan aims at restoring the route and transform it into a walking tour.
The Karakoram Highway
Completed in 1979 and opened to the public in 1985, the Karakoram Highway, formally known as the China-Pakistan Friendship Highway, is a 1,300km road which links Hasan Abdal (located a few kilometers beyond Islamabad, the capital of Pakistan) with Kashgar, the second most important city in Xinjiang province, China.
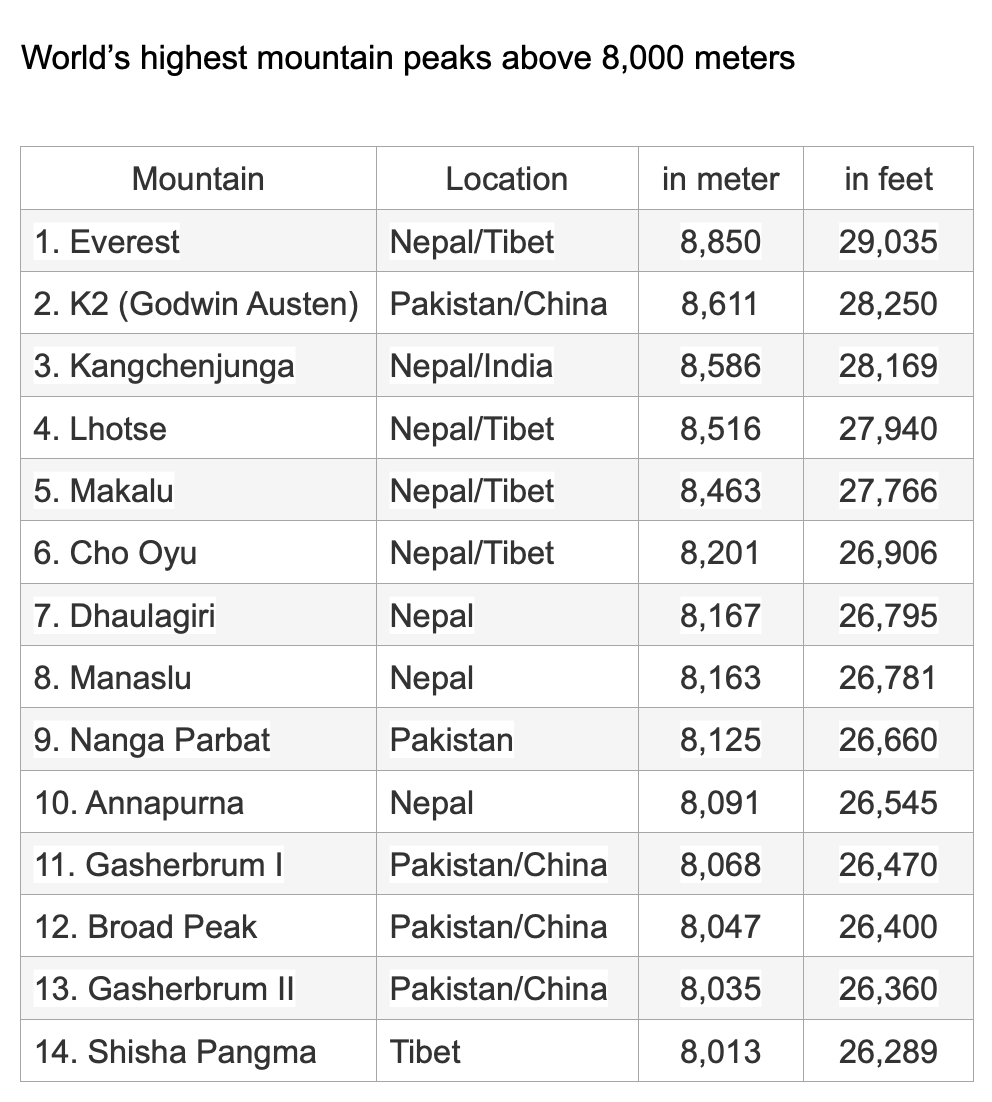
What was once an important ”Silk Road” route which used to link the Indian sub-continent with China, is today considered the 8th wonder of the world, since the altitude and the hard conditions in which it was built made it become an architectonic masterpiece. Therefore, the Karakoram Highway has attracted travelers from all over the world for decades; not only because it is the highest paved road in the world (4,800m at Khunjerab Pass) but also because it goes through the three greatest mountain ranges on Earth: The Himalayas, the Karakoram and the Hindu Kush. The Karakoram Highway is, perhaps, one of the only places in the world where you can admire a mountain 8,000 meters high, like Nanga Parbat, from the window of your car.
The Karakoram Road is, definitely, the most epic road trip ever.
Moreover, these colossal mountains and the huge contrasting landscapes are not the only reason for going on such a journey.
Along the way, you will pass through an endless number of regions, where a large number of ethnic and religious groups live: from the Punjabis in the center of Pakistan to the Ismailis in Hunza, the Tajiks in Tashgurkan and, of course, the Uyghurs in Xinjiang.
Traveling along the Karakoram Highway is like going on a journey through several tiny countries, whose inhabitants will bless you with their hospitality. Depicted here on the map is the section crossing Northern Pakistan.
La Polynésie française (French Polynesia)
The 118 islands of French Polynesia is scattered over 5.5 million square kilometres in the Pacific Ocean (roughly the size of Europe). The islands are grouped in 5 archipelagoes: Archipel de la Société (Iles Du Vent and Iles Sous Le Vent), Archipel des Gambier, Archipel des Australes, Archipel des Tuamotu and Archipel des Marquises. Papeete, the capital city is located on the island of Tahiti (Iles Du Vent, Archipel de la Société). The climat is tropical, with a wet and hot season followed by a dry and mild season. The weather is generally slightly cooler in the Marquises and Australes. The population is made of about 280,000 people comprising Polynesian (84%), French/European (11%) and 5% Asian/Chinese. While French is the official language, most of the Polynesian population speaks a Polynesian dialect. Tourism is the largest industry, and Bora Bora continues to inspire travellers seeking the ultimate paradisiac adventure.
La route Napoleon
History begins on March 1st, 1815, when Napoleon Bonaparte first set foot on Golfe-Juan beach, after one year of exile. By his side, 1200 men ready to conquer Paris and sit their emperor on the throne once again.
It marks the beginning of a six day and 324 kilometre epic journey. At the time, Napoleon and his men took the direction of the Alps and followed the muleteers footpaths to avoid being detected by the royalist resistance. The "Route Napoleon", officially named in 1932, religiously follows a part of his itinerary, going through two regions (Provence-Alps-Côte d'Azur and Rhône-Alpes) and four departments (Alpes Maritimes, Alpes de Haute-Provence, Hautes-Alpes and Isère).
From Vallauris Golfe-Juan to Castellane:
Mythical starting point of the journey, Vallauris Golfe-Juan holds a reconstitution of Bonaparte's landing on the beach every year, at the begining of March. Gradually leaving the seaside, the itinerary goes through several typical Provence villages, such as Cannes and Grasse.
From Castellane to Gap:
As soon as the army advances inlands, altitude becomes apparent. Catellane city, near the Gorges du Verdon, is an important stage before going though the difficult col des Lèques. Following the Durance, the troops reach Dignes, Sisteron and Gap where the terrain becomes more and more uneven, and hilly.
From Gap to Grenoble:
Once Gap is reached, the Alps finally appear. Kilometre after kilometre, Napoleon is reassured at finding that his popularity remains intact. If one place had to be remembered, it would be the town of Laffrey. This is where at the " prairie de la rencontre ", the futur emperor will summon the royal army to join his own troops.
This symbolic victory will lead him to Paris.
Corsica, an island in the Mediterranean Sea, is a captivating destination that boasts stunning natural landscapes and a rich cultural heritage. With its rugged mountains, pristine beaches, and charming towns, Corsica offers a unique and unforgettable experience.
The island's mountainous terrain, including the Corsican Alps, showcases breathtaking peaks and deep valleys. Hiking enthusiasts can explore the famous GR20 trail, which winds through Corsica's rugged interior, providing panoramic views of the surrounding landscapes. The coastline of Corsica is equally captivating, with sandy beaches, hidden coves, and dramatic cliffs. Crystal-clear waters invite visitors to swim, snorkel, and relax in the sun.
Corsica's towns and villages are steeped in history and charm. Ajaccio, the capital city, is renowned as the birthplace of Napoleon Bonaparte and features elegant squares and historic sites. Bonifacio, perched on cliffs overlooking the sea, offers a picturesque old town with narrow streets and stunning views. Calvi boasts a beautiful citadel and a lively marina.
Corsican culture is vibrant and distinctive. The Corsican people take great pride in their traditions and language, which has similarities to Italian. Traditional polyphonic singing, a unique form of musical expression, resonates throughout the island. The cuisine of Corsica is a gastronomic delight, with a focus on fresh seafood, local produce, and flavorful dishes that reflect the island's French and Italian influences.
Corsica's allure as a tourist destination lies in its natural beauty, rich history, and warm hospitality. Whether exploring the mountains, relaxing on the beaches, or immersing oneself in the island's cultural heritage, Corsica offers a memorable and enriching experience for visitors.
The Amazon River is the largest river in the world by volume. It stretches across South America with its main stream collecting the water from about 1,100 tributaries as it travels the 6,448km to the Atlantic. Many of these tributaries are amongst the longest rivers in their own rights. The river basin covers over 6.7 million square kilometers, encompassing parts of Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia, and other countries.
The Amazon River and its tributaries flow through dense rainforests, supporting a wide range of flora and fauna. Some of the Amazon's major tributaries include the Japurá, Juruá, Purus, Madeira, and Tapajós rivers.
One of the most significant tributaries is the Negro River, which is known for its dark, tea-like waters that originate from nutrient-rich soils. The Negro joins the Solimões River to form the main stem of the Amazon.
The Amazon River provides many vital ecosystem services to the region, including regulating the climate, replenishing freshwater resources, and supporting the fishing industry. Unfortunately, the river and its tributaries are also facing threats from deforestation, pollution, and illegal mining. Efforts are underway to protect the Amazon and its valuable biodiversity, including the establishment of protected areas and sustainable development initiatives. (extract from Bradt Guide The Amazon)
US states capitals.
Can you name the capital of each state of the USA?